Setup Local Development Environment with Kubernetes and Skaffold
In this blog post, I will explain the ways to setup local development environment using Kubernetes and Skaffold.
If you are deploying application in k8s environments, it would be better if you can deploy and test in similar environments in your local system.
In this blog post we will deploy spring boot applications on k8s cluster and access their services.
Pre-Requisites
Docker
Creating Kubernetes Cluster
We will create Kubernetes cluster by installing the minikube.
minikube is local Kubernetes, focusing on making it easy to learn and develop for Kubernetes.
Installation
To install the minikube on Windows
- Download and run the installer
- Add minikube.exe binary to your path in environment variables
If you are using PowerShell , you can run following commands to install the minikube
New-Item -Path 'c:\' -Name 'minikube' -ItemType Directory -Force
Invoke-WebRequest -OutFile 'c:\minikube\minikube.exe' -Uri 'https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases/latest/download/minikube-windows-amd64.exe' -UseBasicParsingCode language: Java (java)$oldPath = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)
if ($oldPath.Split(';') -inotcontains 'C:\minikube'){ `
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $('{0};C:\minikube' -f $oldPath), [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine) `
}
Code language: Java (java)To install the latest minikube on x86-64 Linux using binary download
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Code language: Java (java)To install the latest minikube on ARM64 Linux using binary download:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-arm64
sudo install minikube-linux-arm64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Code language: Java (java)To install the latest minikube on x86-64 macOS using binary download:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-darwin-amd64
sudo install minikube-darwin-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Code language: Java (java)To install the latest minikube on ARM64 macOS using binary download:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-darwin-arm64
sudo install minikube-darwin-arm64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Code language: Java (java)Start K8S cluster
From a terminal with administrator access, run the following command
minikube start
Code language: Java (java)Interact with K8S cluster
We need to install kubectl to interact with k8s cluster.
We can use one of the option to install the kubectl CLI
Option 1) If you have installed Docker Desktop, kubectl comes with it. You can add <Docker-Installation-Path>\resources\bin directory to path in environment variables.
Option 2) Download the kubectl binary and add installation directory to your path
Option 3) minikube can download the kubectl and we can use it like this:
minikube kubectl -- get po -ACode language: Java (java)If you install kubectl with minikube, you need to prepend every command with “minikube” word.
If you are using linux or mac, you can create alias command like below
alias kubectl="minikube kubectl --"
Code language: Java (java)Switching to minikube context
If you have installed docker desktop, we need to switch the context to minikube context.
You can check the context
$ kubectl config get-contexts
CURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE
* docker-desktop docker-desktop docker-desktop default
minikube minikube minikube defaultCode language: Java (java)In above response star(*) represents the context being used.
To switch to minikube context run following command
If you are using PowerShell
$ minikube docker-env | Invoke-ExpressionCode language: Java (java)You can also use following command
kubectl config use-context minikubeCode language: Java (java)eval $(minikube docker-env)Code language: Java (java)You can verify the context switch by following command.
$ kubectl config current-context
minikubeCode language: Java (java)Developing Spring Boot Applications
Let’s develop 2 sample spring boot applications which we will deploy the on k8s cluster.
Employee Project
Go to start.spring.io and create a employee project.
We will create a sample controller for testing.
package dev.fullstackcode.k8s.employee.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/employee")
public class EmployeeController {
@GetMapping
public String getEmployee() {
return "from employee project";
}
}
Code language: Java (java)Department Project
Go to start.spring.io and create a department project.
We will create a sample controller for testing.
package dev.fullstackcode.k8s.department.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/department")
public class DepartmentController {
@GetMapping
public String getDepartment() {
return "from department project";
}
}
Code language: Java (java)Dockerfile
Spring Boot applications are deployed as docker images on Kubernetes .In k8s they are called pods.
So we need to write Dockerfile to build images.
FROM eclipse-temurin:17.0.6_10-jdk-jammy as build
COPY mvnw ./
COPY pom.xml ./
COPY src src
RUN chmod a+rx mvnw
RUN --mount=type=cache,target=/root/.m2,rw
RUN ./mvnw clean package -DskipTests
FROM eclipse-temurin:17.0.6_10-jdk-jammy
COPY --from=build "./target/*.jar" /app.jar
RUN addgroup --system springboot && adduser --system sbuser && adduser sbuser springboot
USER sbuser
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/app.jar"]Code language: Java (java)Architecture Diagram
Let’s look at the architecture diagram of k8s deployment.
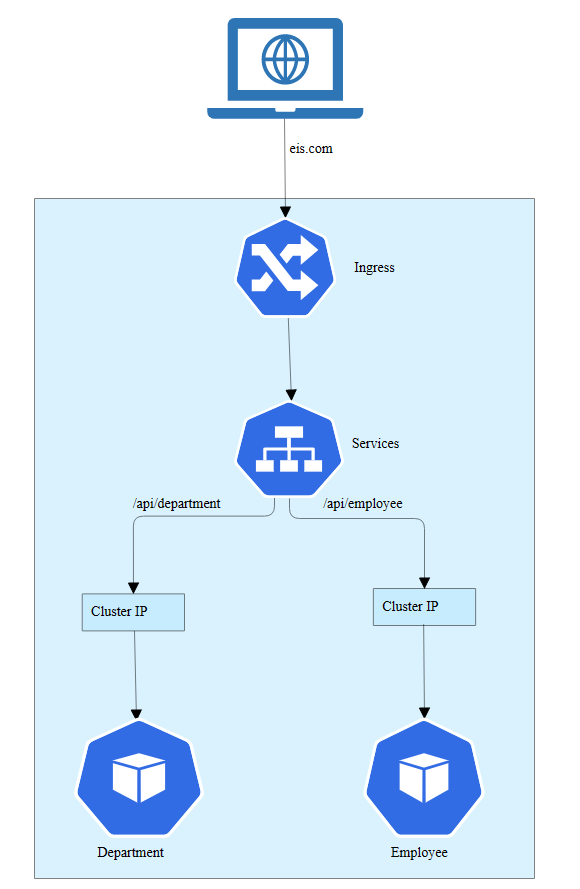
Deployment & Services
A Deployment provides declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.
We can define Deployments to create new ReplicaSets, or to remove existing Deployments and adopt all their resources with new Deployments.
In Kubernetes, a Service is an abstraction which defines a logical set of Pods and a policy by which to access them. It is an abstract way to expose an application running on a set of Pods as a network service.The set of Pods targeted by a Service is usually determined by a selector.
Next we will write Deployment and Service definitions to deploy the applications and expose it as a service.
You can also write Service and Deployment in separate file.
employee-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: department
labels:
app: department
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: department
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: department
spec:
containers:
- image: sureshgkhyd/department
imagePullPolicy: Never
name: department
resources:
limits:
cpu: "250m"
memory: "128Mi"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: department-service
spec:
selector:
app: department
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
Code language: Java (java)department-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: employee
labels:
app: employee
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: employee
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: employee
spec:
containers:
- image: sureshgkhyd/employee
imagePullPolicy: Never
name: employee
resources:
limits:
cpu: "250m"
memory: "128Mi"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: employee-service
spec:
selector:
app: employee
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
Code language: Java (java)Note
Building Docker Images
Since applications are deployed as docker images first we need to create docker images.
docker build . -t sureshgkhyd/employeeCode language: Java (java)docker build . -t sureshgkhyd/departmentCode language: Java (java)Loading docker images to Minikube context
$ minikube image load sureshgkhyd/employee
$ minikube image load sureshgkhyd/departmentCode language: Java (java)Deploying Applications on k8s cluster
kubectl create -f employee-deployment.yamlCode language: Java (java)kubectl create -f department-deployment.yamlCode language: Java (java)Checking deployed pods status
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
department-56c4c968d6-7gmkc 1/1 Running 0 6h57m
employee-5cd898bb84-rc8rt 1/1 Running 0 6h57mCode language: Java (java)Checking deployed services status
$ kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
department-service ClusterIP 10.107.108.26 <none> 8080/TCP 6h59m
employee-service ClusterIP 10.102.201.129 <none> 8080/TCP 6h59m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 7h20mCode language: Java (java)Checking exposed endpoints.
$ kubectl get endpoints --namespace=default
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
department-service 10.244.0.10:8080 7h9m
employee-service 10.244.0.9:8080 7h9m
kubernetes 192.168.58.2:8443 7h30mCode language: Java (java)We have exposed our services as ClusterIP, while these services are communicate each other, they are not exposed to outside world.
To expose these services to outside world we use Ingress Service.
Minikube comes with inbuilt Ingress. we can enable the ingress controller with following command.
minikube addons enable ingress
Code language: Java (java)We can check the Ingress Controller enablement with following command.
$ kubectl get pods --namespace ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ingress-nginx-admission-create-ftkkv 0/1 Completed 0 23h
ingress-nginx-admission-patch-956m7 0/1 Completed 1 23h
ingress-nginx-controller-77669ff58-m5bf4 1/1 Running 0 23h
Code language: Java (java)We will use following Ingress file to expose the services outside world.
Ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-eis
annotations:
# use the shared ingress-nginx
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
spec:
rules:
- host: eis.com
http:
paths:
- path: /api/employee
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: employee-service
port:
number: 8080
- path: /api/department
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: department-service
port:
number: 8080Code language: Java (java)We can check the ingress with following command.
$ kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-eis <none> eis.com 192.168.58.2 80 7h14mCode language: Java (java)Its time to invoke the API which we deployed.
Testing in Windows OS
In windows due to limitation of docker networking, we need to ssh into Ingress controller pod to test the API
To log into ingress controller first we need to switch the namespace to ingress-nginx
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=ingress-nginxCode language: Java (java)Get pods in ingress-nginx namespace
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ingress-nginx-admission-create-ftkkv 0/1 Completed 0 23h
ingress-nginx-admission-patch-956m7 0/1 Completed 1 23h
ingress-nginx-controller-77669ff58-m5bf4 1/1 Running 0 23hCode language: Java (java)SSH into ingress-controller pod
$ kubectl exec ingress-nginx-controller-77669ff58-m5bf4 -it sh
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
/etc/nginx $Code language: Java (java)From the command line
$ curl eis.com/api/employee
from employee project Code language: Java (java) $ curl eis.com/api/department
from department projectCode language: Java (java)Testing in Linux
In Linux, use following command to get the IP on which Ingress is exposed.
$ kubectl get ingress
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress-eis <none> eis.com 192.168.58.2 80 7h14mCode language: Java (java)You can also get IP by using following command
minikube ip
192.168.58.2Code language: Java (java)Now edit your /etc/hosts file
sudo nano /etc/hostsCode language: Java (java)place the following entry and save the file.
192.168.58.2 eis.comCode language: Java (java)Now you can test the API
$ curl eis.com/api/employee
from employee project Code language: Java (java) $ curl eis.com/api/department
from department projectCode language: Java (java)Continuous Development
As we work on the project with every change we need to deploy the project on the k8s cluster for testing.
We use CLI tool called Skaffold to facilitate continuous development.
Skaffold
Skaffold is a command line tool that facilitates continuous development for container based & Kubernetes applications. Skaffold handles the workflow for building, pushing, and deploying your application, and provides building blocks for creating CI/CD pipelines. This enables you to focus on iterating on your application locally while Skaffold continuously deploys to your local or remote Kubernetes cluster, local Docker environment or Cloud Run project.
Installation
Download skaffold and place it in your PATH as skaffold.exe.
Run following command to install Skaffold on Linux
# For Linux x86_64 (amd64)
curl -Lo skaffold https://storage.googleapis.com/skaffold/releases/latest/skaffold-linux-amd64 && \
sudo install skaffold /usr/local/bin/Code language: Java (java)# For Linux ARMv8 (arm64)
curl -Lo skaffold https://storage.googleapis.com/skaffold/releases/latest/skaffold-linux-arm64 && \
sudo install skaffold /usr/local/bin/Code language: Java (java)Run following command to install Skaffold on Mac
# For macOS on x86_64 (amd64)
curl -Lo skaffold https://storage.googleapis.com/skaffold/releases/latest/skaffold-darwin-amd64 && \
sudo install skaffold /usr/local/bin/Code language: Java (java)# For macOS on ARMv8 (arm64)
curl -Lo skaffold https://storage.googleapis.com/skaffold/releases/latest/skaffold-darwin-arm64 && \
sudo install skaffold /usr/local/bin/Code language: Java (java)Initialize Skaffold
We need to go the root of the folder on terminal
Bootstrap Skaffold configuration
- Run the following command to generate a
skaffold.yamlconfig file:
skaffold initCode language: Java (java)2. When prompted to to choose the builder image for each project, select the default option (i.e buildpacks)
? Choose the builder to build image sureshgkhyd/department [Use arrows to move, type to filter]
> Buildpacks (department/pom.xml)
Buildpacks (employee/pom.xml)
Docker (department/Dockerfile)
Docker (employee/Dockerfile)
None (image not built from these sources)
Code language: Java (java)? Choose the builder to build image sureshgkhyd/department Buildpacks (department/pom.xml)
? Choose the builder to build image sureshgkhyd/employee [Use arrows to move, type to filter]
> Buildpacks (employee/pom.xml)
Docker (department/Dockerfile)
Docker (employee/Dockerfile)
None (image not built from these sources)
Code language: Java (java)3. When asked which builders you would like to create Kubernetes resources for, press enter to accept the default selection
? Choose the builder to build image sureshgkhyd/department Buildpacks (department/pom.xml)
? Choose the builder to build image sureshgkhyd/employee Buildpacks (employee/pom.xml)
? Which builders would you like to create kubernetes resources for? [Use arrows to move, space to select, <right> to all, <left> to none, type to filter]
[] Docker (department/Dockerfile)
[] Docker (employee/Dockerfile)
Code language: Java (java)4.When asked if you want to write this configuration to skaffold.yaml, type “y” for yes.
? Choose the builder to build image sureshgkhyd/department Buildpacks (department/pom.xml)
? Choose the builder to build image sureshgkhyd/employee Buildpacks (employee/pom.xml)
? Which builders would you like to create kubernetes resources for?
apiVersion: skaffold/v4beta2
kind: Config
metadata:
name: docker-k-s
build:
artifacts:
- image: sureshgkhyd/department
context: department
buildpacks:
builder: gcr.io/buildpacks/builder:v1
- image: sureshgkhyd/employee
context: employee
buildpacks:
builder: gcr.io/buildpacks/builder:v1
manifests:
rawYaml:
- definitions/department-deployment.yaml
- definitions/employee-deployment.yaml
- definitions/ingress.yaml
? Do you want to write this configuration to skaffold.yaml? (y/N)
Code language: Java (java)5. skaffold.yaml file will be created in root folder of the project.
apiVersion: skaffold/v4beta2
kind: Config
metadata:
name: docker-k-s
build:
artifacts:
- image: sureshgkhyd/department
context: department
buildpacks:
builder: gcr.io/buildpacks/builder:v1
- image: sureshgkhyd/employee
context: employee
buildpacks:
builder: gcr.io/buildpacks/builder:v1
manifests:
rawYaml:
- definitions/department-deployment.yaml
- definitions/employee-deployment.yaml
- definitions/ingress.yaml
Code language: Java (java)Buildpack by default uses java version11,our project is using Java 17, so we need to edit the skaffold.yaml file so that buildpack uses the Java 17
apiVersion: skaffold/v4beta2
kind: Config
metadata:
name: docker-k-s
build:
artifacts:
- image: sureshgkhyd/department
context: department
buildpacks:
builder: gcr.io/buildpacks/builder:v1
env:
- "GOOGLE_RUNTIME_VERSION=17"
- image: sureshgkhyd/employee
context: employee
buildpacks:
builder: gcr.io/buildpacks/builder:v1
env:
- "GOOGLE_RUNTIME_VERSION=17"
manifests:
rawYaml:
- definitions/department-deployment.yaml
- definitions/employee-deployment.yaml
- definitions/ingress.yaml
Code language: Java (java)Note
Use skaffold dev
Run the following command to begin using Skaffold for continuous development:
skaffold devCode language: Java (java)Skaffold automatically builds and deploys your application.
Skaffold is now watching for any file changes, and will rebuild your application automatically.
Let’s see this in action.
Generating tags...
- sureshgkhyd/department -> sureshgkhyd/department:latest
- sureshgkhyd/employee -> sureshgkhyd/employee:latest
Some taggers failed. Rerun with -vdebug for errors.
Checking cache...
- sureshgkhyd/department: Found Locally
- sureshgkhyd/employee: Found Locally
Tags used in deployment:
- sureshgkhyd/department -> sureshgkhyd/department:ad59aa1419566c49b1637e8be068729676f778f6cfff6a467c620d1a0098cfa4
- sureshgkhyd/employee -> sureshgkhyd/employee:82f2a8add5b81610092a79f91e7505a6a1d4b0234e25d001b514cb6cd415a81a
Starting deploy...
- deployment.apps/department created
- service/department-service created
- deployment.apps/employee created
- service/employee-service created
Waiting for deployments to stabilize...
- ingress-nginx:deployment/department is ready. [1/2 deployment(s) still pending]
- ingress-nginx:deployment/employee is ready.
Deployments stabilized in 2.883 seconds
Listing files to watch...
- sureshgkhyd/department
- sureshgkhyd/employee
Press Ctrl+C to exit
Watching for changes...
[employee]
[employee] . ____ _ __ _ _
[employee] /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
[employee] ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
[employee] \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
[employee] ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
[employee] =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
[employee] :: Spring Boot :: (v3.0.2)
[employee]
[department]
[department] . ____ _ __ _ _
[department] /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
[department] ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
[department] \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
[department] ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
[department] =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
[department] :: Spring Boot :: (v3.0.2)
[department]
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:03.569Z INFO 1 --- [ main] d.f.k8s.employee.EmployeeApplication : Starting EmployeeApplication v0.0.1-SNAPSHOT using Java 17.0.6 with PID 1 (/app.jar started by sbuser in /)
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:03.574Z INFO 1 --- [ main] d.f.k8s.employee.EmployeeApplication : No active profile set, falling back to 1 default profile: "default"
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:04.371Z INFO 1 --- [ main] d.f.k.department.DepartmentApplication : Starting DepartmentApplication v0.0.1-SNAPSHOT using Java 17.0.6 with PID 1 (/app.jar started by sbuser in /)
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:04.474Z INFO 1 --- [ main] d.f.k.department.DepartmentApplication : No active profile set, falling back to 1 default profile: "default"
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:24.366Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:24.375Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:24.567Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:24.568Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/10.1.5]
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:24.582Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:24.583Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/10.1.5]
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:26.971Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:26.973Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:27.067Z INFO 1 --- [ main] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 22403 ms
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:27.069Z INFO 1 --- [ main] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 21503 ms
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:37.188Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:37.472Z INFO 1 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
[department] 2023-02-12T09:38:37.484Z INFO 1 --- [ main] d.f.k.department.DepartmentApplication : Started DepartmentApplication in 40.406 seconds (process running for 48.793)
[employee] 2023-02-12T09:38:37.670Z INFO 1 --- [ main] d.f.k8s.employee.EmployeeApplication : Started EmployeeApplication in 40.704 seconds (process running for 48.979)
Code language: Java (java)Now let’s edit the response of one of controller
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/employee")
public class EmployeeController {
@GetMapping
public String getEmployee() {
return "from employee project - updated";
}
}
Code language: Java (java)Noe Skaffold identifies that one of the file has changed and re-builds the docker images and redeploys the images on k8s cluster.
Now if you test the employee api again you should see the updated response.
$ curl eis.com/api/employee
from employee project - updatedCode language: Java (java)You can download the sourcecode of the project from GitHub